Tag Archive for: ethics

Featured Collaborator for March: Dorothee Baumann-Pauly
Blog Interview with Dorothee Baumann-Pauly, Research Director at the NYU Stern Center for Business and Human Rights
Interview with Dorothee Baumann-Pauly, Research Director at the NYU Stern Center for Business and Human Rights
How does your work on human rights help companies that want to improve themselves as ethical systems?
In contrast to the more established, yet still vague framework, of corporate social responsibility (CSR), business and human rights (BHR) explicitly focuses on aligning companies’ core business processes with their commitment to human rights. Thus, BHR asks how companies are making their money, not how they are spending it. Human rights challenges are real for multinational companies; they pose major business risks to their operations. Companies today are expected to commit to respecting human rights in their business operations, and they need concrete standards that clarify what this commitment means in their operational context. The requirement to report against a specific standard increases transparency over a corporation’s human rights conduct and creates incentives to develop enduring ethical systems.

Strategy and Business Interview: Jonathan Haidt
Blog Jonathan Haidt, Thomas Cooley Professor of Ethical Leadership at New York University's Stern School of Business, was interviewed by strategy+business and shares his insight and expertise on ethical systems design and the various initiatives of our organization.
Jonathan Haidt, Thomas Cooley Professor of Ethical Leadership at New York University's Stern School of Business, was interviewed by strategy+business and shares his insight and expertise on ethical systems design and the various initiatives of our organization.
What causes a company to undermine its own future through ethical missteps? What enables it to lie to regulators, conceal critical data, and take chances on fraudulent activity that might, sooner or later, come to light? Is it the rapacious nature of capitalism itself, as some believe? Is it the work of a few “bad apples,” unavoidable in a milieu of dynamic innovation? Or is it some innate aspect of human behavior, impossible to regulate completely, but possible to understand? This inquiry, framed by New York University professor Jonathan Haidt and a global network of colleagues, could help keep companies out of trouble in the future — or perhaps change our view of what trouble really means.
Continue reading this in-depth interview with Jonathan Haidt >>

Featured Collaborator for February: Steven Blader
BlogInterview with Steven Blader, associate professor of Management and Organizations at New York University's Stern School of Business.

Can fairness motivate ethical decision making or do most people look out for fairness as a one way street: to ensure they are treated like they imagine they deserve to be.
There is an extraordinary amount of evidence that people’s concern about fairness is much more than simply a tool they may use to help them get what they feel they deserve or want. For instance, we often see people defining and evaluating fairness independently of their outcome concerns; reacting more strongly to fairness than to their self-interest; and evaluating and reacting to fairness even as third parties to an encounter and thus when their own outcomes are not involved.
These and other findings confirm to us that people’s concern about fairness is genuine, distinct, and pervasive. As such, fairness can absolutely provide a route to enhancing ethicality in both one’s own, as well as other’s, decision making. That said, there are factors that make the picture more complicated, factors that must be considered when turning to fairness as a route to enhancing ethicality.

Is Political Ideology a Compliance and Ethics Risk?
Blog Cross posted with permission from ES Collaborator Jeffrey Kaplan's Conflict of Interest blog
Cross posted with permission from ES Collaborator Jeffrey Kaplan's Conflict of Interest blog
In a post last week on the Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance and Financial Regulation, Danling Jiang, Associate Professor of Finance at Florida State University, summarizes a recent article she authored with Irena Hutton, Associate Professor of Finance at Florida State University; and Alok Kumar, Professor of Finance at the University of Miami: “Political Values, Culture, and Corporate Litigation,” which was published in the latest issue of Management Science and which “examine[s] whether the political culture of a firm defines its ethical and legal boundaries as observed by the propensity for corporate misconduct.”
In a post last week on the Harvard Law School Forum on Corporate Governance and Financial Regulation, Danling Jiang, Associate Professor of Finance at Florida State University said of recent research, “Using one of the largest samples of litigation data to date, [they] show that firms with Republican culture are more likely to be the subject of civil rights, labor, and environmental litigation than Democratic firms, consistent with the Democratic ideology that emphasizes equal rights, labor rights, and environmental protection. However, firms with Democratic culture are more likely to be the subject of litigation related to securities fraud and intellectual property rights violations than Republican firms whose Party ideology stresses self-reliance, property rights, market discipline, and limited government regulation.”
This is interesting – if not necessarily surprising – stuff, and particularly so in an election year. But does it bear on the work of C&E professionals? And does it have anything to do with conflicts of interest?

David Mayer Writes For Fast Company
Blog David Mayer, associate professor of management and organizations at the University of Michigan's Stephen M. Ross School of Business has recently signed on as a monthly contributor to Fast Company, writing about business ethics and leadership.
David Mayer, associate professor of management and organizations at the University of Michigan's Stephen M. Ross School of Business has recently signed on as a monthly contributor to Fast Company, writing about business ethics and leadership.
From their website: Fast Company "is the world's leading progressive business media brand, with a unique editorial focus on innovation in technology, ethical economics, leadership, and design."

Ethical Systems Lands 8 of the Top 100 Most Influential in Business Ethics
Blog Each year, Ethisphere recognizes 100 individuals that have made a material impact in the world of business ethics through their annual 100 Most Influential People in Business Ethics list.
Each year, Ethisphere recognizes 100 individuals that have made a material impact in the world of business ethics through their annual 100 Most Influential People in Business Ethics list.
Ethical Systems collaborators have long been featured on this prestigious list. This year, however, is the first we have had 8 of our distinguished leaders included at one time.

Featured Collaborator for January: Robert Frank
Blog Interview with Robert Frank, the H. J. Louis Professor of Management and Professor of Economics at Cornell University's Johnson Graduate School of Management, author and New York Times columnist
Interview with Robert Frank, the H. J. Louis Professor of Management and Professor of Economics at Cornell University's Johnson Graduate School of Management, author and New York Times columnist
What are your main areas of research?
When I was recently asked to offer a short course based on my work, I chose “Rivalry and Cooperation” as my title, since these two themes have dominated my research for more than three decades.
My focus on rivalry springs from the fact that humans evolved under extremely competitive conditions in which local rank was often the best predictor of who would survive and prosper. When there wasn’t enough food to go around, for example, the lowest-ranked individuals were most likely to starve, and in early polygynous societies, high-ranking males were most likely to claim multiple wives. So rivalry—competition for relative position—has always been a central feature of human interaction. This strand of my work has explored the consequences of concerns about relative position for a range of important outcomes, including the kinds of things we buy, the kinds of jobs we prefer, the behaviors we choose to regulate, and the tax systems we adopt.

Your Permanent Record: Blacklist for ethics gaining steam
Blog Bad ethics should not be forgotten in the new year- or any other- as bankers and regulators discussed creating an ethical blacklist for individuals working at regulated financial institutions, at the NY Federal Reserve‘s recent culture conference.
Bad ethics should not be forgotten in the new year- or any other- as bankers and regulators discussed creating an ethical blacklist for individuals working at regulated financial institutions, at the NY Federal Reserve‘s recent culture conference.
This signals new enthusiasm for a provocative proposal originally suggested in 2014 by Bill Dudley, President of the NY Fed: When an employee leaves a company, the organization would have a mandate to report information relating to his/her misconduct to a central database. Concerning hiring decisions, all firms would have a reciprocal duty to check the database against their potential hire list. The goal is to stem the tide of bad apples that bounce from firm-to-firm, negatively influencing stability, profits and planning.

Ethical Systems Year End Letter from Jon Haidt
Blog Dear Friends,
Dear Friends,
Ethical Systems reflects on a year marked by tragedy and triumph, major ethics news and new research. We began 2015 by receiving IRS recognition of our organization as a 501c3 non-profit, and filing our first 990 report. Finally, we can begin raising money to fund our operations. What started as an informal collaborative network of researchers has blossomed into an official organization uniting researchers and business leaders who want to change the business world by “making ethics easy.”
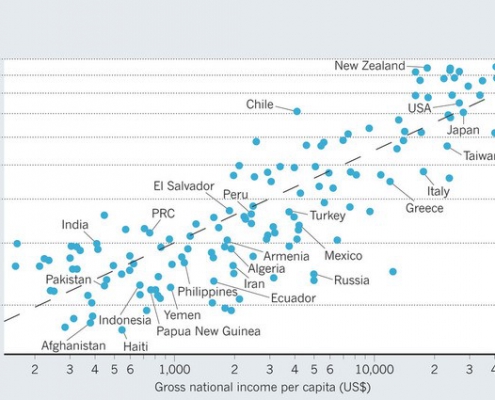
Earthquakes and Shaky Ethics: The Perils of Construction Corruption
Blog A study in Nature shows that our planet has a lot to teach us about business ethics. While we know that ethics pays, what is also now clear is that the absence of ethics can kill.
A study in Nature shows that our planet has a lot to teach us about business ethics. While we know that ethics pays, what is also now clear is that the absence of ethics can kill.
Nicholas Ambraseys of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Imperial College London and Roger Bilham from the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences and the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Colorado, Boulder compared deaths from earthquakes and found that “83% of all deaths from building collapse in earthquakes over the past 30 years occurred in countries that are anomalously corrupt.” This is all the more staggering when you consider that the researchers removed any contributing factors, such as poor building materials, from their analysis.
The construction industry is an industry both highly valued and highly susceptible to corruption. Governments, regulators, businesses and workers all have a vested interest in reducing and eliminating bribery and other practices that put people at risk. Without a systemic approach to reducing corruption and improving ethics, it won’t just be buildings that crumble; trust, stability and the long-term viability of a governmental body also risk imminent collapse.
